Cheap Living Abroad for Americans
This is a practical Thailand relocation guide for Americans who are seriously considering a move, not just a vacation. If you are researching moving to Thailand from USA, trying to relocate to Thailand, or planning long-term living in Thailand as an American, this page gives you the full framework.
Thailand is not difficult to move to. But it rewards preparation and punishes assumptions. The lifestyle can be significantly cheaper than the U.S., but only if you understand visas, taxes, healthcare, and city choice before you land.
This page works as your central roadmap. Each section connects to deeper guides.
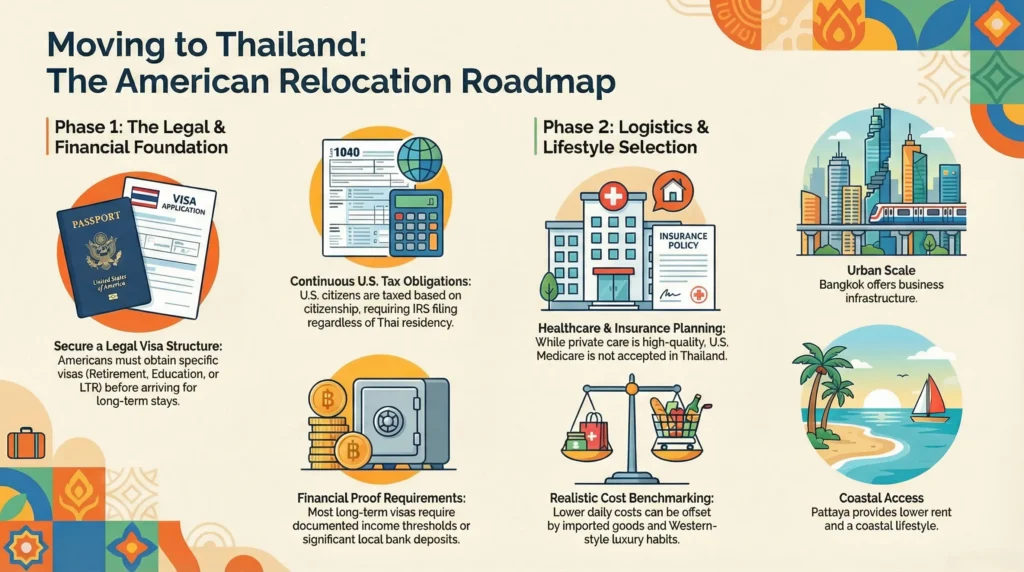
Before you relocate to Thailand, you need a legal structure. Americans cannot simply arrive and stay long term without the correct visa.
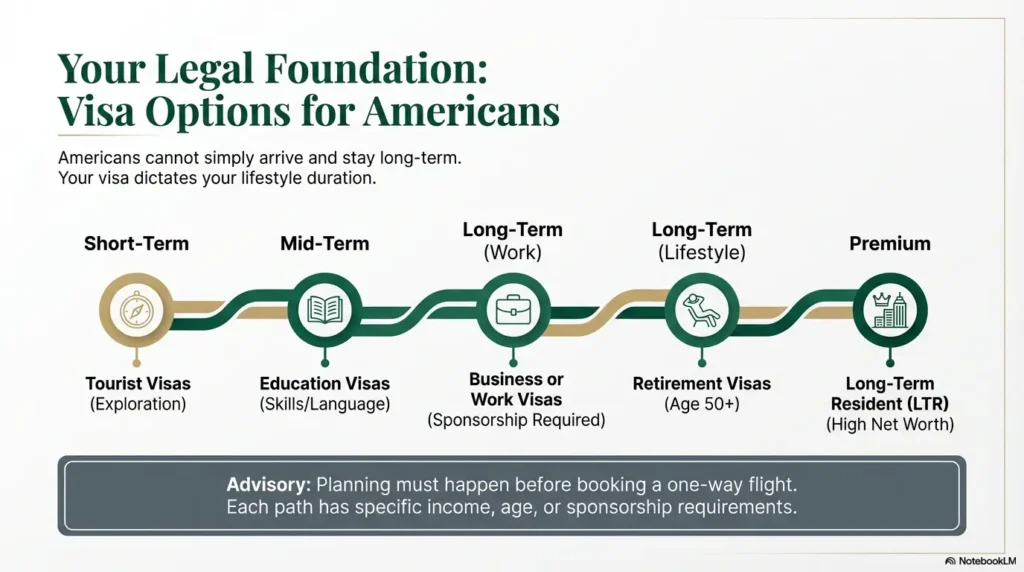
The most common paths include:
- Tourist visas for short-term stays
- Education visas
- Business or work visas
- Retirement visas
- Long-term resident options
Each visa type has different income, age, or sponsorship requirements. If you are moving to Thailand from USA, visa planning should happen before booking a one-way flight.
Read the full breakdown:
→ Thailand Visa Guide for Americans (2026)
One of the main reasons Americans relocate to Thailand is cost. Compared to most U.S. cities, housing, food, and daily services are significantly lower.
But “cheap” depends on lifestyle.
Living in Bangkok in a modern condo is very different from renting in Pattaya or Chiang Mai. Imported goods, Western restaurants, and nightlife can quickly narrow the savings gap.
If you are serious about living in Thailand as an American, you need a realistic monthly structure, not just YouTube estimates.

See detailed numbers here:
→ Cost of Living in Thailand (2026)
Thailand has a strong private healthcare system. Major hospitals in Bangkok and Pattaya offer international-level service at a fraction of U.S. pricing.
But Americans relocating need insurance planning. U.S. Medicare does not apply overseas. Travel insurance is not long-term health insurance.
Private plans vary based on age, coverage level, and pre-existing conditions. For retirees, this is one of the most important financial variables.
Read more:
→ Healthcare Costs in Thailand for Americans
U.S. citizens are taxed based on citizenship, not residence. That means filing U.S. taxes continues even after relocation.
Thailand also has its own tax rules depending on residency status and income source.
Understanding the Foreign Earned Income Exclusion, double taxation treaties, and local reporting obligations is critical before you relocate to Thailand.
Full tax overview:
→ U.S. Taxes While Living in Thailand

City choice changes everything.
Bangkok offers scale, infrastructure, and business opportunities. Pattaya offers lower rent, compact living, and coastal access.
For Americans deciding between the two, the real difference is lifestyle density versus urban scale.
Compare both here:
→ Bangkok vs Pattaya: Where Should You Live?
Thailand remains one of the more popular destinations for Americans looking to retire abroad.
The retire in Thailand guide process usually involves a retirement visa, financial proof requirements, and long-term housing planning.
Lower healthcare costs, warm climate, and slower pace attract retirees. But paperwork, insurance, and income thresholds must be handled correctly.
Full retirement breakdown:
→ Retire in Thailand Guide (2026)

Most relocation problems are preventable.
Common issues include:
Relocating is not difficult. But it requires structure.
If you are serious about moving to Thailand from USA, treat the move like a financial decision, not an extended vacation.
This Thailand relocation guide is your starting point.