Cheap Living Abroad for Americans

This guide explains Thailand retirement visa financial requirements for foreigners who need exact income thresholds, proof rules, cost structures, and long-term financial realities before applying.
Thailand offers retirement visas to foreigners age 50 or older who can prove stable finances and meet immigration screening standards.
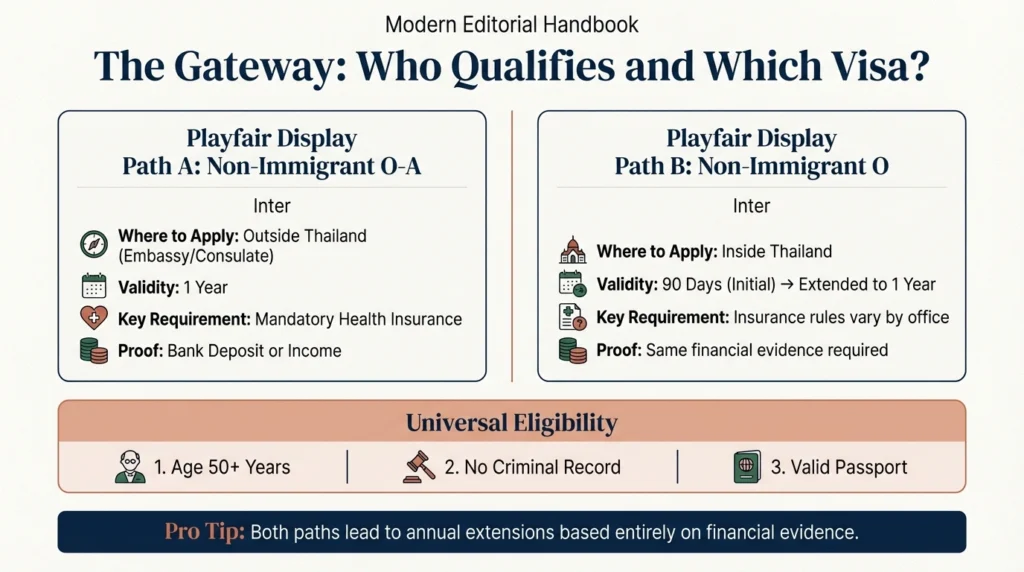
Both lead to annual extensions based entirely on financial evidence.
Thailand immigration accepts three financial methods. Applicants must choose one.
You must maintain:
- 800,000 THB in a Thai bank account
- About $22,500 USD
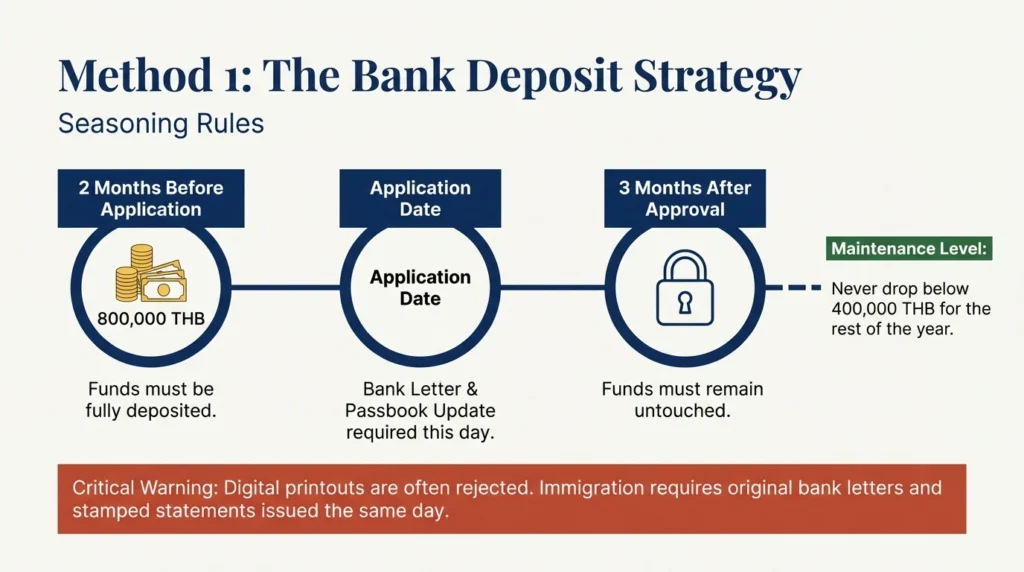
Rules:
Immigration checks bank letters and stamped statements. Digital printouts are rejected at many offices.
You must prove:
- 65,000 THB monthly income
- About $1,800 USD per month
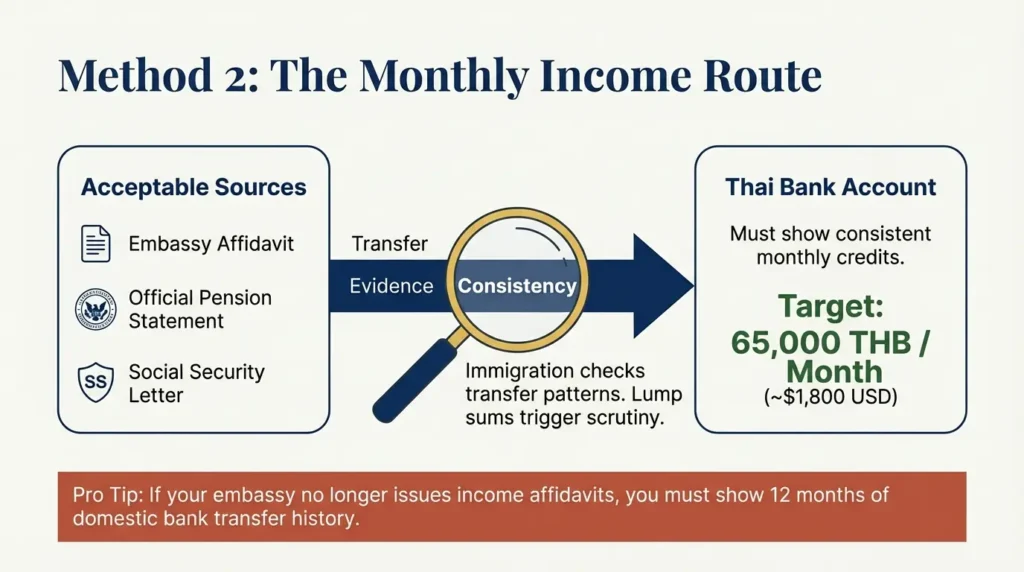
Proof methods accepted:
- Embassy income affidavit if available
- Pension statements
- Social Security letters
- Bank transfers showing monthly deposits
Immigration wants consistent deposits. Lump sums often trigger questions.
You can combine income and savings.

Example:
- Bank savings 400,000 THB
- Annual income 400,000 THB
This method is common for retirees with modest pensions.
Applicants often underestimate documentation standards. Immigration offices verify more than totals.
Required financial proof:
- Bank letter issued same day as application
- Updated passbook pages
- Certified bank statements
- Income proof originals
- Embassy certification if used
Photocopies without certification are rejected.
Some offices call banks to verify balances. Others check transfer patterns to confirm real income.
Financial proof affects approval speed more than paperwork volume.
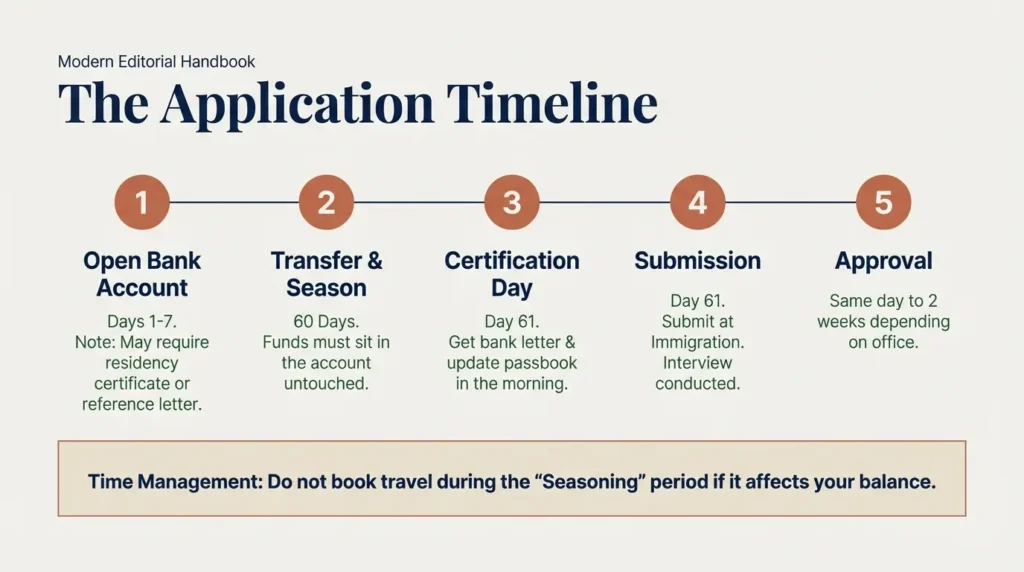
Process:
- Open Thai bank account
- Transfer required funds
- Wait required seasoning period
- Obtain bank certification letter
- Submit visa application
- Attend immigration interview
- Receive approval stamp
Typical processing time:
| Stage | Time |
|---|---|
| Bank account opening | 1 to 7 days |
| Fund seasoning | 60 days |
| Immigration processing | Same day to 2 weeks |
Visa cost is not the main expense. Compliance costs accumulate yearly.
| visa | Cost THB | USD |
|---|---|---|
| Initial visa fee | 2,000 | $55 |
| Annual extension | 1,900 | $52 |
| Re-entry permit | 1,000 | $27 |
| Multiple re-entry | 3,800 | $105 |
| letters | Typical Cost |
|---|---|
| Bank certification letter | $3 to $6 |
| Statement printing | $2 to $5 |
| Notary or certification | $10 to $25 |
Required for O-A visa holders.
| Age | Annual Premium |
|---|---|
| 50–60 | $800 to $1,500 |
| 60–70 | $1,600 to $3,000 |
| 70+ | $3,500 to $6,000 |
Insurance is often the largest recurring cost for retirees.
Financial requirements only show minimum eligibility. Real living costs matter more.
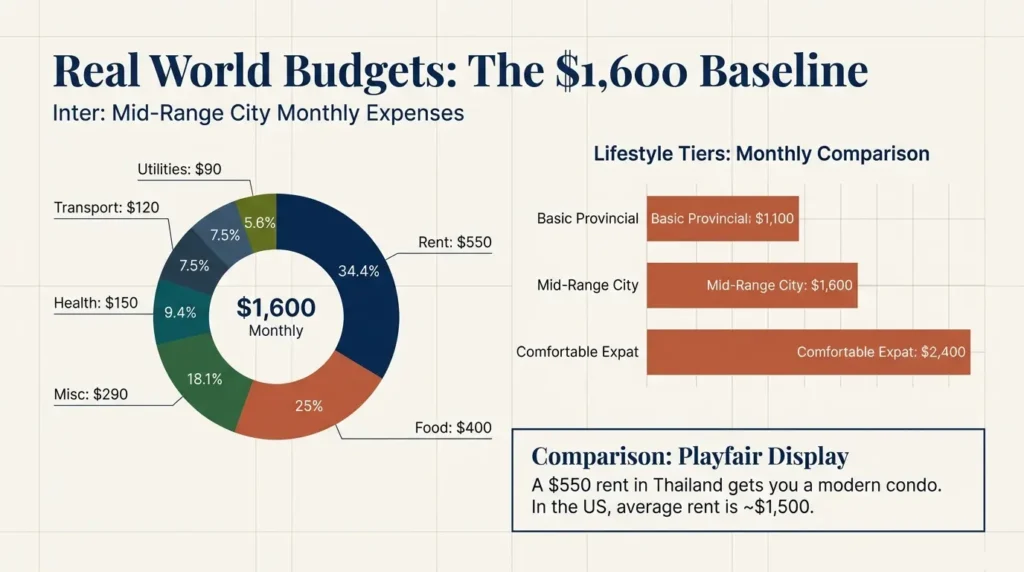
Typical monthly budgets:
| Lifestyle | Monthly Cost USD |
|---|---|
| Basic provincial | $1,100 |
| Mid-range city | $1,600 |
| Comfortable expat | $2,400 |
Breakdown example for $1,600 budget:
Immigration does not assess living expenses. They only verify financial thresholds.
Some retirees choose alternatives with different financial rules.
| Visa | Deposit Requirement | Income Requirement | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Retirement Visa | $22,500 | $1,800/mo | Annual renewal |
| LTR Wealthy Pensioner | $80,000 assets | $40,000 income | 10-year visa |
| Elite Visa | None | None | Pay fee instead |
Retirement visa remains the lowest financial entry path.
Medical cost matters because insurance is optional for some visa types but medical bills are not.
Typical private hospital prices:
| Treatment | Cost USD |
|---|---|
| Doctor visit | $25 to $60 |
| MRI scan | $300 to $900 |
| Hospital night | $150 to $500 |
| Minor surgery | $1,200 to $4,000 |
Many retirees choose insurance until age 70 then self-insure using savings.
Thailand taxes residents on locally earned income. Foreign income rules depend on remittance timing and residency status.
Important facts:
- U.S. citizens must file U.S. taxes regardless of residence
- Social Security often remains taxable in U.S.
- Thailand does not tax foreign pensions if not remitted same year under current interpretation
Tax treaties exist but do not remove filing obligations.
CLICK HERE TO LEARN MORE ABOUT TAXES .
Immigration rarely denies retirees for age or paperwork. Most rejections come from financial errors.
Common mistakes:
Depositing funds too late
Using borrowed money
Inconsistent income deposits
Missing bank certification
Incorrect balance duration
Officers check transaction history. Sudden large transfers before application can lead to rejection.
The annual extension process requires structured documentation and timing discipline.
A full step-by-step breakdown is explained in the Thailand visa renewal process for Americans guide.
You must:
- Maintain minimum bank balance after approval
- Provide updated statements yearly
- Repeat income verification
- Show residence address
Dropping below required balance before renewal can void eligibility.
Income: $2,100 per month
Savings: $10,000
Outcome:
Qualifies using income method. No large deposit required.
Income: none
Savings: $50,000
Outcome:
Deposit method works. Must keep 800,000 THB in Thai bank yearly.
Income: $1,000/month
Savings: $15,000
Outcome:
Combination method allowed. Must show annual total equals 800,000 THB.
Opening a Thai bank account is not automatic.
Possible requirements:
- Local address
- Visa type
- Reference letter
- Minimum deposit
Branch discretion matters. Some branches refuse foreigners while others approve same day.
Retirement visas are conditional status, not residency.
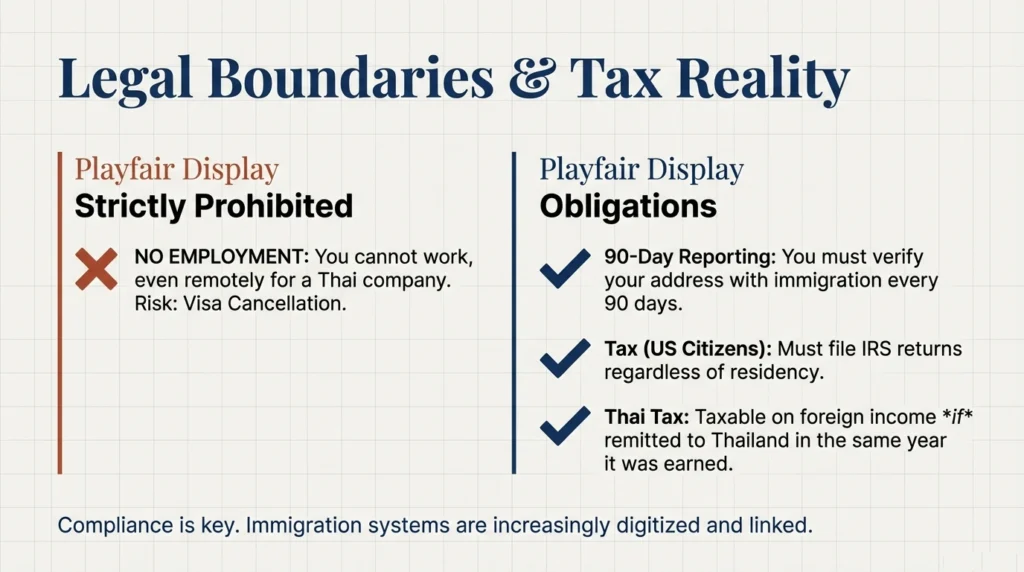
Limitations:
- Cannot legally work
- Must report address every 90 days
- Must maintain financial proof
- Must renew yearly
Failure to meet financial rules cancels extension.
| Expense | Thailand | U.S. Average |
|---|---|---|
| Rent | $550 | $1,500 |
| Doctor visit | $40 | $180 |
| Meal | $3 to $8 | $15 to $25 |
| Utilities | $90 | $220 |
Financial thresholds for visas look high but daily living costs are lower than U.S. averages.
Serious applicants should review the full Thailand Relocation Guide before choosing a visa route. It outlines banking, housing contracts, tax setup, and healthcare decisions in correct order.
This article is based on official regulations and publicly available government sources:
Financial thresholds reflect officially published 800,000 THB deposit or 65,000 THB monthly income requirements enforced by Thai Immigration.
You need 800,000 THB or about $22,500 USD deposited in a Thai bank account. Funds must be there at least two months before application and cannot drop below required levels during the year.
Yes. Immigration accepts Social Security as proof if you show official statements and consistent monthly transfers into your Thai account.
No. After approval you can reduce the balance to 400,000 THB, but you must restore it before renewal and meet timing rules again.
Insurance is mandatory for O-A visas. Extensions inside Thailand may not require it, but medical costs without coverage can be high.
No. Any employment violates visa conditions and can lead to cancellation.
The income method is usually cheapest. If your pension exceeds 65,000 THB per month, you do not need a large bank deposit.
This guide explains how to show income proof for Thailand retirement visa, including accepted income sources, document standards, bank verification…
This guide explains the Thailand visa renewal process for Americans, including required financial proof, extension costs, income requirements, bank documentation,…