Cheap Living Abroad for Americans

This guide explains how to show income proof for Thailand retirement visa, including accepted income sources, document standards, bank verification rules, cost breakdown, renewal procedures, tax clarity, and common rejection reasons Americans face.
This applies to retirement extensions based on the monthly income method.
To qualify using income instead of savings, you must show:
65,000 THB per month
Approximately $1,800 USD per month
Annual equivalent:
780,000 THB per year
Approximately $21,600 USD
Official criteria are published by the Thai Immigration Bureau.
Income must be consistent and verifiable.
Immigration evaluates source credibility before amount.
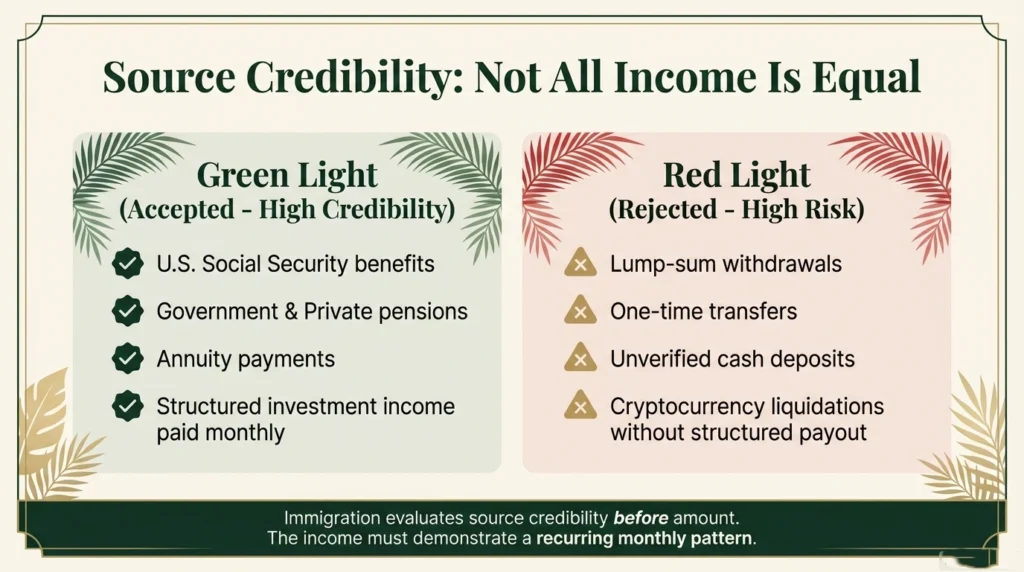
Accepted income sources:
- U.S. Social Security benefits
- Government pensions
- Private pensions
- Annuity payments
- Structured investment income paid monthly
Not accepted alone:
- Lump-sum withdrawals
- One-time transfers
- Unverified cash deposits
Income must show recurring monthly pattern.
For full financial threshold details, review Thailand retirement visa financial requirements inside the Retirement & Long-Term Living section.
Immigration requires certified documentation.
- Official pension or Social Security letter
- Recent bank statements showing monthly deposits
- Same-day Thai bank certification letter
- Updated passbook pages
- Passport copies
Embassy income affidavits are no longer issued by some embassies. Bank deposit history is now the primary proof method.
Income must appear in a Thai bank account.
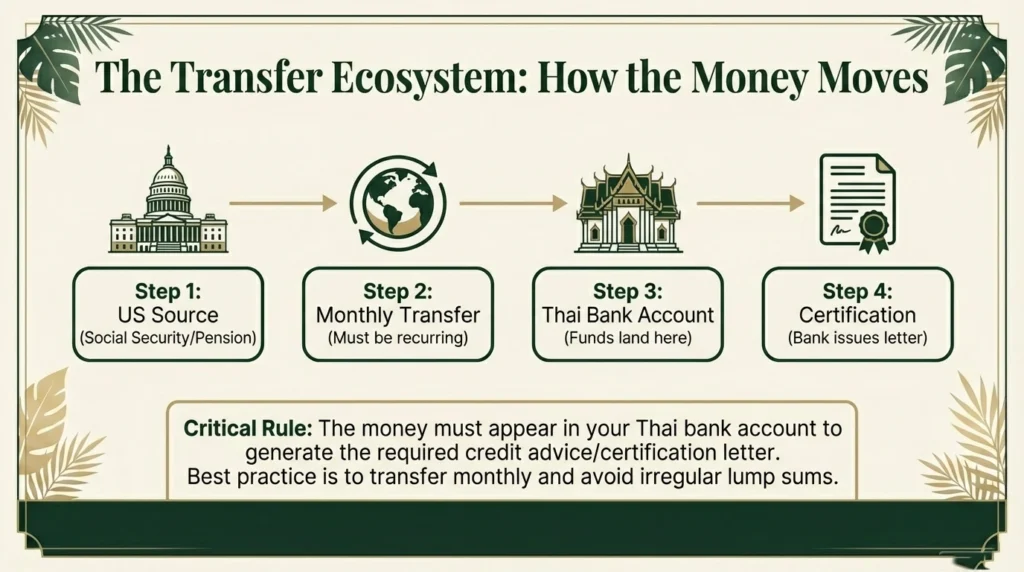
Best practice:
- Transfer monthly into your Thai account
- Maintain deposit amount at or above 65,000 THB equivalent
- Avoid irregular lump-sum transfers
Exchange rate fluctuations can reduce deposit below required threshold.
Example:
If USD weakens, $1,800 may convert to less than 65,000 THB.
Consistent margin above minimum reduces risk.
Income qualification avoids locking $22,500 but still has costs.
| – | THB | USD |
|---|---|---|
| Extension fee | 1,900 | $52 |
| Bank certification | 100–200 | $3–6 |
| Statement printing | 100 | $3 |
| Photos and copies | 100 | $3 |
Estimated annual compliance cost: $60–90
| Category | Income Method | Deposit Method |
|---|---|---|
| Monthly proof required | Yes | No |
| Capital lock | None | $22,500 |
| Scrutiny level | Higher | Lower |
| Exchange rate exposure | Yes | No |
| Liquidity impact | Low | High |
If comparing both methods, review Can Americans Use Savings for Thailand Retirement Visa for full breakdown.
Immigration reviews recent months before renewal.
If any month falls below 65,000 THB equivalent:
- Officers may question qualification
- You may need to supplement with savings
- Renewal can be delayed
Maintaining $2,000 monthly equivalent provides safety margin.
You must prove income every year.
Renewal requires:
- Updated pension statements
- Recent Thai bank statements
- Fresh bank certification letter
- Address verification
Past approval does not guarantee future approval.
Income qualification does not cover medical expenses.
Typical private hospital pricing:
| Treatment | USD |
|---|---|
| Doctor visit | $30–60 |
| MRI | $300–900 |
| Hospital night | $150–500 |
(Hospital pricing example.)
Insurance for retirees 60–70 often costs $1,600–3,000 annually.
Healthcare costs without insurance can exceed annual extension fees quickly.
Income proof does not change tax obligations.

Americans must:
- File U.S. tax returns annually
- Report foreign bank accounts if required
- Monitor Thai tax residency exposure
(Thai Revenue Department reference.)
Social Security may remain taxable in the U.S. even if living abroad.
Visa status does not eliminate U.S. reporting requirements.
Monthly benefit: $1,950
Converts above 65,000 THB
Qualifies if transferred monthly.
Pension: $1,200
Dividends: $800
Total: $2,000
Qualifies if both sources documented and deposited regularly.
Variable deposits
Often rejected due to inconsistency.
Income must appear structured and stable.
- Depositing once every few months
- Not maintaining Thai bank account
- Relying solely on U.S. statements
- Ignoring exchange rate drop
- Missing bank certification letter
Most income proof problems are not caused by earning too little.
They are caused by how the income is documented and transferred.
The most common mistake is irregular deposits.
Immigration expects to see a clear, consistent monthly pattern that aligns with the 65,000 THB requirement.
If you transfer money every two or three months in larger amounts, officers may question whether the income is truly structured retirement income or simply discretionary savings being moved around.
Another frequent issue is relying only on U.S. pension statements.
Showing a Social Security letter is not enough on its own.
Immigration wants to see the funds physically arriving in your Thai bank account.
Matching monthly deposits inside Thailand are critical.
Exchange rate fluctuation creates hidden risk.
If you transfer exactly $1,800 and the dollar weakens that month, your deposit may convert below 65,000 THB.
Even a small shortfall can complicate renewal.
Maintaining a margin above the minimum reduces exposure.
I have personally met retirees in Thailand who were fully qualified on paper.
They had legitimate pensions and long-term retirement visas.
But because they skipped a month of transfers, consolidated payments, or relied on irregular dividend income, renewal became stressful.
The income was real.
The pattern was not structured correctly.
Another mistake is failing to obtain a same-day bank certification letter.
Immigration officers do not rely solely on printed statements.
They often require official bank confirmation issued the day of application.
The underlying reality is simple.
Immigration evaluates consistency, traceability, and timing more than headline income amount.
A disciplined monthly transfer schedule, properly stamped statements, and proactive exchange rate monitoring prevent most income-based renewal problems before they start.
Income qualification works best if:
- You receive steady pension
- You prefer liquidity over large deposit
- You do not want $22,500 locked in Thai bank
- You are comfortable with annual documentation
If planning long-term retirement relocation, review the Thailand Relocation Guide before choosing income versus deposit method.
You must show official pension or Social Security documents and matching monthly deposits of at least 65,000 THB into your Thai bank account.
Yes. Social Security qualifies if documented and deposited consistently.
You may need to transfer additional funds. Falling below threshold can cause renewal problems.
Not necessarily. Many immigration offices now rely primarily on bank deposit history.
Yes. Annual income plus bank balance must equal 800,000 THB.
Yes in liquidity terms. You avoid locking $22,500 but must provide stronger documentation yearly.
This guide explains Thailand retirement visa financial requirements for foreigners who need exact income thresholds, proof rules, cost structures, and…
This guide explains the Thailand visa renewal process for Americans, including required financial proof, extension costs, income requirements, bank documentation,…